Dissolving Features
“Dissolving” is the process of aggregating, or generalizing, features within a vector layer based on one or more shared attribute values.
Included in this tutorial:
Comparing the Dissolve Tool and Pairwise Dissolve Tool
Dissolving Features with the Pairwise Dissolve Tool, with an example, and examining the results.
Software version in examples: ArcGIS Pro 3.4.2
Tutorial Data: The tutorial includes demonstration with sample data available here.
Credits: L. Meisterlin (2025)
There are two tools to dissolve features in ArcGIS Pro (Dissolve and Pairwise Dissolve). This tutorial briefly compares the two, then demonstrates dissolving features with an example.
Comparing the Dissolve Tool and the Pairwise Dissolve Tool
The two tools are almost identical in functionality. Their primary differences are:
The Pairwise Dissolve tool is optimized to take advantage of parallel processing, and thus can run faster than its older counterpart.
The Dissolve tool has one extra option (outputting unsplit lines) that may be relevant if you are dissolving line features.
Accessing the tools
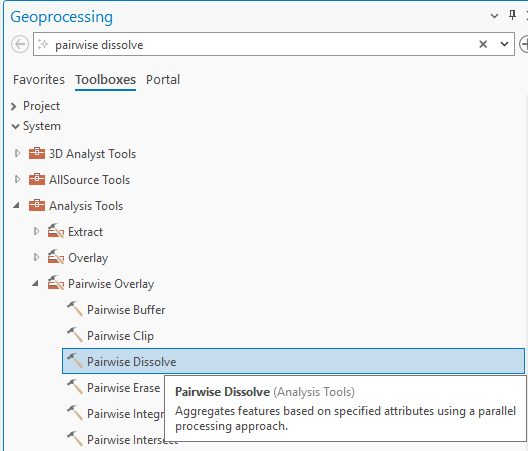
You can find the newer Pairwise Dissolve tool within the Geoprocessing toolboxes under Analysis Tools > Pairwise Overlay > Pairwise Dissolve. (This can be a little confusing, given that most of us do not consider dissolving as an “overlay” operation.)
You can find the original Dissolve tool within the Geoprocessing toolboxes under Data Management Tools > Generalization > Dissolve.
As with all other tools, you can find either by using the Geoprocessing pane’s search bar.
the Pairwise Dissolve tool’s location
the Dissolve tool’s location
Comparing Parameters and Options
As noted above, their inputs are practically identical with the one exception of the classic Dissolve tool’s “Unsplit lines” option.
the Pairwise Dissolve tool
the Dissolve tool’s location
Here is a breakdown of the parameters:
Input Features: the vector layer with features that will be aggregated or “dissolved”
Output Feature Class: the name and location of the new vector layer that will be created
Dissolve Field(s): the attribute field(s) with the values that will determine which features are aggregated. The tool will aggregate (combine) features with the same value in the field(s) selected.
TIP: To dissolve all features within the input layer into one single feature, leave the Dissolve Field(s) option empty.
Statistics FIeld(s): Here you can optionally choose one or more fields with values that will be summarized in the output feature class. Under Field, specify the relevant attribute table field. Under Statistic Type, choose the summary statistic to calculate.
Create Multipart Features (checkbox): If checked, the tool will generate “multipart features” aggregating all features with shared values in the Dissolve Field(s), regardless of their adjacency. If unchecked, the tool will not create multipart features, and only adjacent features with shared values will be aggregated.
Unsplit Lines (checkbox; Dissolve tool only): If you are dissolving line features, this option is similar to the multipart features option. If checked, line features with a shared value in the Dissolve Field(s) will only be dissolved/aggregated if they also share an endpoint. If unchecked, line features with a shared value in the Dissolve Field(s) will be aggregated into a single feature regardless of their geometry.
Example: Dissolving Polygon Features with the Pairwise Dissolve Tool
To demonstrate a dissolving operation, we are using a polygon layer (called “blocks_prj”) as the Input Features.
In this example, we are aggregating features based on the value in the CT2010 attribute field (the “Dissolve Field(s)”). Features with the same value in this field will be aggregated together. In the screenshot below, this field is highlighted in the layer’s attribute table.
For demonstration, we calculate the sum of the “Shape_Area” for each of the features combined in our output. Thus, the Statistic Field is “Shape_Area” and its Statistic Type is “Sum.”
The input parameters are set in the screenshot below.
getting ready to dissolve the block features based on their CT2010 values
Examining the result
The result of the example operation is shown below. The new layer is symbolized as thick outlines to show the smaller, original polygons that have been aggregated into larger, dissolved polygons by the operation. One example dissolved polygon feature is selected/highlighted in the map view and in the attribute table.
In the attribute table, the Dissolve field (“CT2010”) is maintained in the output. The calculated statistic–the sum of the input layer’s “Shape_Area” field values–is also found in the output attribute table as a new field (called “SUM_Shape_Area”.) Both of these fields are highlighted in the image below.
the results of the dissolved features